Tooling and Equipment in Forging are essential components in the metal shaping process, as they apply the compressive forces needed to transform raw materials into durable and precisely shaped parts. The success of any forging operation heavily depends on the quality and suitability of the tooling and equipment in forging used.
There are several primary types of tooling and equipment in forging, including forging hammers, forging presses, and upsetting machines. Each type of equipment serves a unique function and is paired with specialized tooling to optimize the forging process.
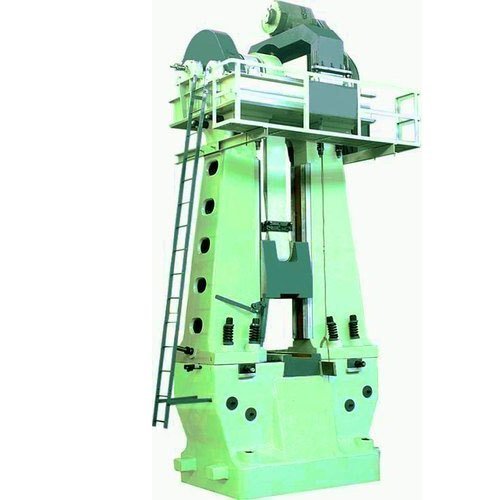
Forging hammers, such as drop hammers and power hammers, are a key part of tooling and equipment in forging. These hammers deliver high-impact blows to the metal workpiece, making them ideal for closed-die forging operations that require rapid shaping under repeated impacts. The tooling used with forging hammers includes robust dies made from high-strength tool steels that must withstand intense forces and high temperatures.
On the other hand, forging presses represent another crucial category within the tooling and equipment in forging spectrum. Presses apply a steady, controlled pressure rather than impact, which is beneficial for open-die forging and precision forging processes. The tooling for forging presses is designed to provide high accuracy and excellent control over material deformation, enabling the production of complex parts with consistent quality.
Upsetting machines form a specialized subset of tooling and equipment in forging. These machines are designed to increase the diameter of metal components, such as bolts and shafts, by compressing their length. The tooling for upsetting involves dies and collars that ensure uniform shaping during this compressive process.
Effective tooling and equipment in forging also includes auxiliary devices like heating furnaces, mandrels, and fixtures that support and enhance the main forging operations. Proper maintenance and design of tooling and equipment in forging not only improve part quality but also extend the life of the tooling, reducing downtime and operational costs.
In modern forging facilities, advancements in tooling and equipment in forging have led to increased automation, better die materials, and enhanced precision controls. These improvements allow for more efficient production runs and higher-quality forged components.
To summarize, the role of tooling and equipment in forging cannot be overstated. The choice of equipment—whether forging hammers, presses, or upsetting machines—and their corresponding tooling directly influence the mechanical properties, dimensional accuracy, and surface finish of forged parts.
Ultimately, successful forging operations rely on a comprehensive understanding of tooling and equipment in forging to match the correct tools with the right forging process, ensuring optimal results for every application.
Forging Equipments
Forging equipment is essential for shaping metal by applying compressive forces. The primary types of equipment include forging hammers, presses, and upsetting machines.
Forging hammers (like drop hammers and power hammers) deliver high-impact blows to shape metal and are often used in closed-die forging.
Forging presses apply steady pressure and are ideal for open-die and precision forging, offering better control over the deformation process.
Upsetting machines increase the diameter of metal parts and are commonly used for bolts and shafts.

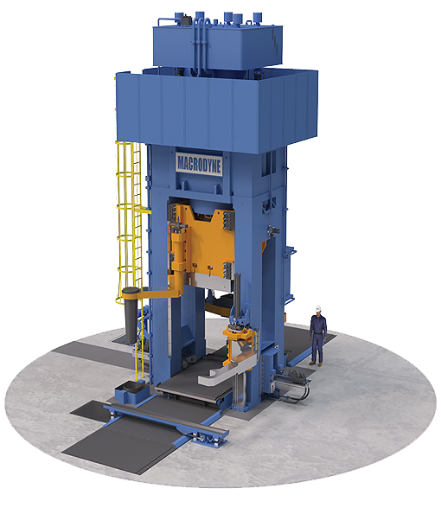
Heating Equipments
Heating equipment in forging is used to raise the temperature of metal workpieces to make them malleable for deformation. Proper heating is crucial to reduce resistance to deformation, prevent cracking, and improve material flow.
The most commonly used heating equipment includes:
Forging Furnaces: These can be gas-fired, oil-fired, or electric, and are used to uniformly heat metal billets or ingots to forging temperatures (typically between 950°C and 1250°C for steel).
Induction Heaters: Use electromagnetic fields to rapidly and efficiently heat metal parts. They provide precise, localized heating and are widely used in automated and high-volume forging operations.

Tooling
- Forging Dies
- Punches and Drifts
- Bolsters and Die Holders
Forging Dies
Open-Die Dies: Simple flat or contoured dies used to shape large, unconfined metal workpieces.
Closed-Die (Impression) Dies: Precisely shaped dies that fully enclose the metal, forming it into final or near-net shapes.
Insert Dies: Replaceable die inserts fitted into larger die blocks, designed to reduce wear and lower tooling costs.
Mandrels and Plugs
These are used to support and shape hollow parts such as rings and tubes during forging operations.Punches and Drifts
Punches: Used to create holes or indentations in the workpiece.
Drifts: Employed to expand or finish holes to the desired dimensions.
Bolsters and Die Holders
These components provide structural support and maintain the proper alignment of dies within forging machines.Lubricants and Die Coatings
Applied to reduce friction and tool wear, facilitate smoother metal flow, and enhance die life and product quality.

Handling Equipments
Handling equipment in forging is used to safely move, position, and hold hot metal workpieces during the forging process. These tools are essential for maintaining operator safety, improving efficiency, and ensuring accurate forging operations.
Tongs
Manually operated tools used to grip and hold hot metal pieces. They come in various shapes and sizes depending on the workpiece geometry.Manipulators
Mechanized or hydraulic machines that can lift, rotate, and position heavy or hot workpieces with precision. They are commonly used in large-scale or automated forging setups.Lifting Cranes and Hoists
Used to transport large billets or forged components within the forging facility. Overhead cranes are especially common in heavy forging operations.Roller Tables and Conveyors
Facilitate the movement of hot metal between different stages of the forging process, such as from the furnace to the hammer or press.Robotic Arms
Automated arms used in high-volume production for precise and repeatable handling of workpieces, improving both speed and safety.

Cooling System
In forging, cooling systems play a crucial role in managing the temperature of tools, dies, and sometimes even the forged parts themselves. Proper cooling is essential—it helps extend the life of the dies, keeps the equipment from overheating, and ensures that the final product maintains its shape and quality.
Water Cooling Systems
These systems use built-in channels within dies or tools to circulate water and carry away excess heat. They’re especially common in closed-die forging, where temperature control is critical for precision and consistency.
Air and Air-Mist Cooling
Instead of water, some setups use compressed air or a mist made from air and water to cool down hot surfaces. This method is useful when direct water contact might cause damage or is otherwise not suitable.
Cooling Jackets
These are external covers that circulate cooling fluid around components like press columns or large tools. They help prevent overheating, especially during continuous or heavy-duty forging operations.


